- Biophotonic Therapy is the use of light to activate the healing properties of the blood. BT is photomedicine and has a well-characterized clinical profile. A dozen books and some 400 articles in the German, Russian, and English-language medical literature describe Biophotonic Therapy. Other common names for BT are Ultraviolet Blood Irradiation and Photoluminescence Therapy.
- In BT’s extracorporeal form, ultraviolet and visible light are used to treat a small amount of blood, which is then reinfused.
- In BT’s intravenous form, a low-intensity laser (generally at 632.8 nm) shines through a waveguide inside a needle into the blood. BT can also be administered sublingually.
10 Key Points about Biophotonic Therapy
Rethinking Biophotonic Therapy
 In this video, Tom Lowe, director of Physicians Awareness UBI, and Kenneth J. Dillon, author of Healing Photons, discuss the history, science, challenges, and promise of Biophotonic Therapy. Also known as ultraviolet blood irradiation, BT treats small amounts of blood with light in extracorporeal or intravenous modes. BT was invented by Emmet Knott in the 1920s. Hundreds of clinical studies have shown its effectiveness in various indications, e.g., against childhood asthma. Thousands of practitioners around the world use it to treat a wide range of disorders. BT is the leading phototherapeutic treatment of infectious diseases.
In this video, Tom Lowe, director of Physicians Awareness UBI, and Kenneth J. Dillon, author of Healing Photons, discuss the history, science, challenges, and promise of Biophotonic Therapy. Also known as ultraviolet blood irradiation, BT treats small amounts of blood with light in extracorporeal or intravenous modes. BT was invented by Emmet Knott in the 1920s. Hundreds of clinical studies have shown its effectiveness in various indications, e.g., against childhood asthma. Thousands of practitioners around the world use it to treat a wide range of disorders. BT is the leading phototherapeutic treatment of infectious diseases.
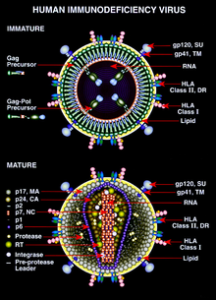 Amid the fanfare regarding initiatives to treat the devastating HIV/AIDS epidemic, a noteworthy finding has been overlooked. After more than two decades of debate, experimentation by patients, and scattered clinical testing of non-drug therapies of HIV, we now know much better which ones actually work.
Amid the fanfare regarding initiatives to treat the devastating HIV/AIDS epidemic, a noteworthy finding has been overlooked. After more than two decades of debate, experimentation by patients, and scattered clinical testing of non-drug therapies of HIV, we now know much better which ones actually work.