- Biophotonic Therapy is the use of light to activate the healing properties of the blood. BT is photomedicine and has a well-characterized clinical profile. A dozen books and some 400 articles in the German, Russian, and English-language medical literature describe Biophotonic Therapy. Other common names for BT are Ultraviolet Blood Irradiation and Photoluminescence Therapy.
- In BT’s extracorporeal form, ultraviolet and visible light are used to treat a small amount of blood, which is then reinfused.
- In BT’s intravenous form, a low-intensity laser (generally at 632.8 nm) shines through a waveguide inside a needle into the blood. BT can also be administered sublingually.
 [For a fuller discussion of Biophotonic Therapy and the underlying science, including citations to the medical literature, see Healing Photons: The Science and Art of Blood Irradiation Therapy. For a brief discussion, see 10 Key Points about Biophotonic Therapy. See also the video Rethinking Biophotonic Therapy.]
[For a fuller discussion of Biophotonic Therapy and the underlying science, including citations to the medical literature, see Healing Photons: The Science and Art of Blood Irradiation Therapy. For a brief discussion, see 10 Key Points about Biophotonic Therapy. See also the video Rethinking Biophotonic Therapy.]
Overview
Biophotonic Therapy uses light in an extracorporeal or intravenous mode to activate the red blood cells, a form of immunity inherited from humankind’s distant oligocellular ancestors. BT has an instructive 80-year history (see below); a range of modalities; well-characterized mechanisms of action; a wide array of indications; several counterindications; well-understood, limited side-effects in certain cases; and a scientific literature that now includes some 400 articles as well as a dozen books. No drug resistance to BT has ever been reported.
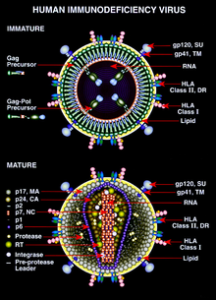 Amid the fanfare regarding initiatives to treat the devastating HIV/AIDS epidemic, a noteworthy finding has been overlooked. After more than two decades of debate, experimentation by patients, and scattered clinical testing of non-drug therapies of HIV, we now know much better which ones actually work.
Amid the fanfare regarding initiatives to treat the devastating HIV/AIDS epidemic, a noteworthy finding has been overlooked. After more than two decades of debate, experimentation by patients, and scattered clinical testing of non-drug therapies of HIV, we now know much better which ones actually work.
