 Sekhmet (“The Mighty One”), lioness goddess of ancient Egypt, spread terror with her bloody rampages. Yet she became the protector of kings and a favorite personal goddess of millions of Egyptians.
Sekhmet (“The Mighty One”), lioness goddess of ancient Egypt, spread terror with her bloody rampages. Yet she became the protector of kings and a favorite personal goddess of millions of Egyptians.
Why did Egyptians have a goddess who required such assiduous and even obsessive propitiation? Why did other Egyptian goddesses play roles similar to Sekhmet’s? What explains Sekhmet’s dual nature as destroyer and protector? Why did Egyptians call her the Eye of Ra? Why did she originally appear with an oval disk on her head?
We now have good answers to these questions. But in order to understand them, we need to see why we should think that Sekhmet was Planet Venus. And that requires us to investigate a major case of scientific rejectionism.
Tags: Ancient Egypt, Bastet, Bronze Age catastrophes, Egyptian medicine, Hathor, isis, Mars, Mut, myth, Ra, Sekhmet, Tefnut, Velikovsky, venus
 There are good reasons to think that Earth has turned over on various occasions. But who can be surprised that this perception—so removed from everyday experience—seems less than instantaneously persuasive?
There are good reasons to think that Earth has turned over on various occasions. But who can be surprised that this perception—so removed from everyday experience—seems less than instantaneously persuasive?
The good reasons include telling evidence in narrative testimony and correctly interpreted myths of the ancients, embedded patterns in ancient cultures that give evidence of inversions, and the insights and arguments of two formidable researchers. Now we can: add new reasons that strengthen the case; specify the approximate dates of four inversions; extend the theory to the five great mass extinctions of prehistory; comprehend that Earth is actually prone to inversion; and point to where to find more evidence. Understanding inversions helps us correct errors in interpreting past planetary and Earth science while providing clues relevant to climate change.
Tags: Ancient China, Archer Yi, Bronze Age catastrophes, Earth, geomagnetism, inversion of Earth, magnetic reversals, Mars, mass extinctions, Pacific Basin, terrestrial, tippe top, Velikovsky, venus, Warlow
 Based on his interpretation of ancient sources, Immanuel Velikovsky argued famously that Venus had emerged from Jupiter as a comet; interacted with the Earth and Mars in the second and first millennia BC, causing the Bronze Age catastrophes; and then finally settled into a nearly circular orbit of the Sun.
Based on his interpretation of ancient sources, Immanuel Velikovsky argued famously that Venus had emerged from Jupiter as a comet; interacted with the Earth and Mars in the second and first millennia BC, causing the Bronze Age catastrophes; and then finally settled into a nearly circular orbit of the Sun.
Three lines of reasoning support a Revised Venus Theory.
First, instead of the various unpersuasive suggestions that Velikovsky and others have made for how a cometary Venus could have emerged from Jupiter, we should consider the possible consequences of the immense gravitational field of Jupiter, which pulls toward it a stream of asteroids and comets, as with Shoemaker-Levy 9 in 1994.
Tags: Abu Simbel, Athena, Black Drop, Great Serpent Mound, Jupiter, Mars, Metis, Nefertari, planetary science, Poseidon, Ramses II, tidal locking, Velikovsky, venus, Zeus
 What reality lay behind ancient China’s flood legends? Who was the Yellow Emperor? Who was Archer Yi, what was his vermilion bow, how did he shoot down nine of ten suns, and why were there ten suns in the first place?
What reality lay behind ancient China’s flood legends? Who was the Yellow Emperor? Who was Archer Yi, what was his vermilion bow, how did he shoot down nine of ten suns, and why were there ten suns in the first place?
We now know the answers to these and other questions about ancient China. These answers can lead us to a new understanding of Chinese history, of the worldwide Bronze Age catastrophes, and of the history of climate change. (Ma Yuan, The Yellow River Breaches Its Course, Wikimedia Commons)
Tags: Ancient China, archaeoastronomy, Archer Yi, Bronze Age catastrophes, climate change, Jingwei bird, Liangzhu, Longshan, Mars, myth, Shang, stone ladders, Taidong, Taosi, Teotihuacan, tsunamis, Velikovsky, venus, Western Zhou, Xia, Yellow Emperor, 灾难和气候变化中国古代
 Once a leading theory of the origin of the Earth-Moon system, the Capture Theory is simple and intuitively plausible. The numerous instances of moons with retrograde orbits show that capture is fairly common. The lunar orbit’s three moments of inertia are consistent with a past very eccentric orbit, suggestive of capture. However, the Moon would have to come from a different part of the solar system to account for its very depleted iron compared to the Earth’s iron, which means that it would approach the Earth at a high velocity that would prevent capture. Researchers have searched in vain for a braking mechanism that would slow it down so it could be captured. Still, the accumulated evidence and arguments make the Capture Theory a viable one.
Once a leading theory of the origin of the Earth-Moon system, the Capture Theory is simple and intuitively plausible. The numerous instances of moons with retrograde orbits show that capture is fairly common. The lunar orbit’s three moments of inertia are consistent with a past very eccentric orbit, suggestive of capture. However, the Moon would have to come from a different part of the solar system to account for its very depleted iron compared to the Earth’s iron, which means that it would approach the Earth at a high velocity that would prevent capture. Researchers have searched in vain for a braking mechanism that would slow it down so it could be captured. Still, the accumulated evidence and arguments make the Capture Theory a viable one.
But
Tags: Capture theory, Earth, earth science, Earth-Moon system, Giant Impact, Jupiter, Mars, Mercury, moon, origin of Earth, origin of Mars, origin of the Moon, Outer Solar System Origin of the Terrestrial Planets, oxygen isotope ratios, planetary science
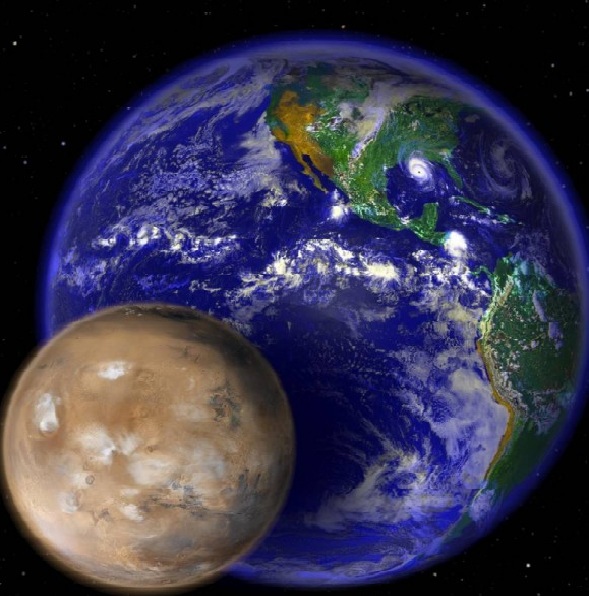 There’s no shortage of candidates for the cause of the mass extinctions of prehistory. But experts have found flaws in every one.
There’s no shortage of candidates for the cause of the mass extinctions of prehistory. But experts have found flaws in every one.
Asteroid impact at Chicxulub, Yucatan clearly played a role in the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction that wiped out the non-flying dinosaurs 66,000,000 years ago, though scientists point to the serious disruptions that had begun hundreds of thousands of years before with the basalt flows of the Deccan Traps. Giant basalt lava flows that poisoned the atmosphere and oceans played a role in four or perhaps all five major extinctions. But other enormous basalt flows have not caused extinctions, nor did they cause the tsunamis associated with various extinctions. Researchers have suggested many other mechanisms, but there’s no consensus at all.
Lurking in the background, however, is a quite plausible cause, one that would have possessed the power to set off the volcanic activity, air pollution, mass wasting, sea level shifts, loss of oxygen in oceans, climate changes, and other phenomena associated with the extinctions.
The Martian Theory
Tags: catastrophe, Chicxulub, climate change, Deccan Traps, dinosaurs, earth science, extinctions, geology, great mass extinctions, Mars, paleontology, planetary science, prehistory, tsunamis, Valles Marineris
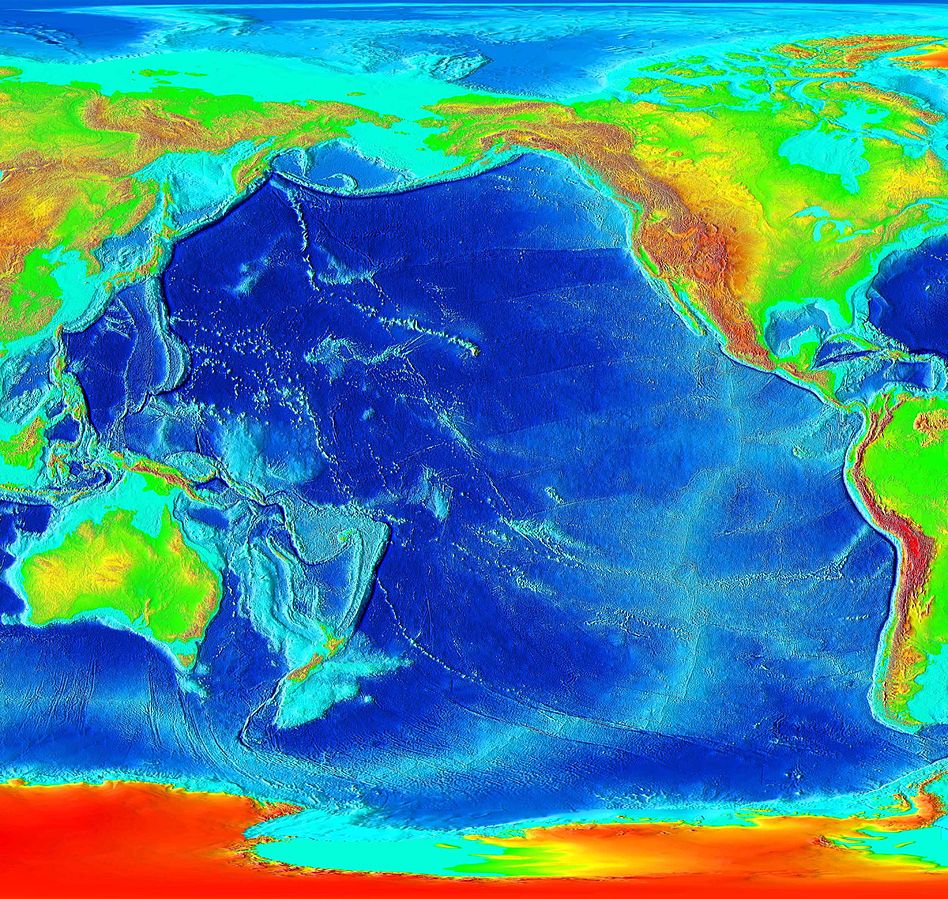
There are good reasons to think that Earth and Mars originally formed a single planet outside the orbit of Jupiter. Early in Solar System history, Jupiter’s powerful gravitational field pulled this planet past the gas giant. As the planet neared Jupiter, tidal friction heated it to the melting point, and Jupiter tore Mars away from Earth, leaving the Pacific Basin and an array of evidence on both planets. Earth and Mars then sped off into the inner solar system.
originally formed a single planet outside the orbit of Jupiter. Early in Solar System history, Jupiter’s powerful gravitational field pulled this planet past the gas giant. As the planet neared Jupiter, tidal friction heated it to the melting point, and Jupiter tore Mars away from Earth, leaving the Pacific Basin and an array of evidence on both planets. Earth and Mars then sped off into the inner solar system.
How Do We Know This?
Tags: Earth, earth science, geomagnetism, Hawaiian Islands, hotspots, Mars, moon, Pacific, planetary science, plate tectonics, plumes, seismography, volcanism
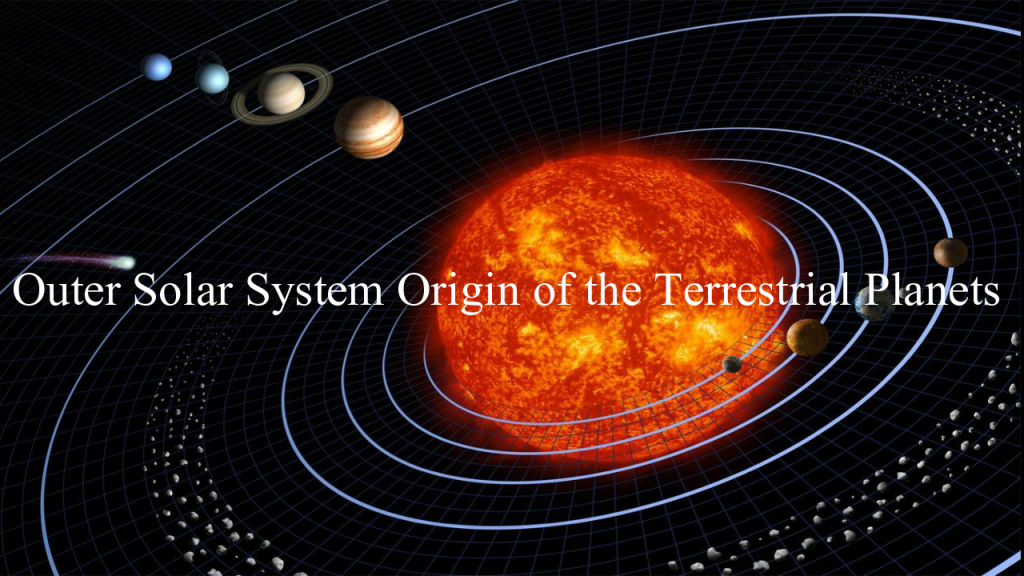
Historian and scientific researcher Kenneth J. Dillon discusses his theory The Outer Solar System Origin of the Terrestrial Planets (OSSO). OSSO explains how Mercury, Earth, the Moon, and Mars originated outside the orbit of Saturn, then were pulled inward by Jupiter’s gravity. Tidal friction heated them to incandescence, then they tidally locked to Jupiter and were separated, moving as comets into their present orbits. See also https://www.scientiapress.com/outer-solar-system-origin.
Outer Solar System Origin of the Terrestrial Planets
Tags: Bronze Age catastrophes, Capture theory, Immanuel Velikovsky, inner solar system, Jupiter, Mars, Mercury, moon, Oceanus Procellarum, planetary science, terrestrial, tidal locking, venus
Historia n and scientific researcher Kenneth J. Dillon explains his The Martian Theory of Mass Extinctions. For most of the past 4 billion years, the orbits of Mars and Earth were more eccentric than at present, and they intersected. The closest approaches of Mars led to the great mass extinctions of prehistory, while more distant approaches might account for many minor extinctions as well. The theory shows why the extinctions were serial events, why they differed in size, how they shaped the surface of Mars, and what made them so terrifically devastating. For further information, see https://www.scientiapress.com/extinctions.
n and scientific researcher Kenneth J. Dillon explains his The Martian Theory of Mass Extinctions. For most of the past 4 billion years, the orbits of Mars and Earth were more eccentric than at present, and they intersected. The closest approaches of Mars led to the great mass extinctions of prehistory, while more distant approaches might account for many minor extinctions as well. The theory shows why the extinctions were serial events, why they differed in size, how they shaped the surface of Mars, and what made them so terrifically devastating. For further information, see https://www.scientiapress.com/extinctions.
The Martian Theory of Mass Extinctions
Tags: Bronze Age catastrophes, Chicxulub, Cretaceous-Paleogene, Deccan Traps, Elysium Mons, inner solar system, Mars, mass extinctions, mass wasting, Olympus Mons, Tharsis, tidal locking, Velikovsky, venus
 The civilizations of Mesoamerica abounded in mysteries. What caused their fixation on Venus? What led them to develop their intricate, highly precise calendars? What can explain the little pecked-cross circles embedded in the landscape? Why were these peoples so keenly bent on human sacrifice? What were the Aztecs referring to when they said that this was the age of the Fifth Sun?
The civilizations of Mesoamerica abounded in mysteries. What caused their fixation on Venus? What led them to develop their intricate, highly precise calendars? What can explain the little pecked-cross circles embedded in the landscape? Why were these peoples so keenly bent on human sacrifice? What were the Aztecs referring to when they said that this was the age of the Fifth Sun?
We have a skeleton key that can unlock these old secrets.
Tags: archaeoastronomy, Aztec, ball game, catastrophes, inversion of Earth, Mars, Maya, Mesoamerica, Olmec, pecked-cross circles, synodical year, Teotihuacan, Toltec, Velikovsky, venus

Decades of meticulous investigation have revealed many features of the 1st Century BC Antikythera Mechanism, a portable planetarium that demonstrated the motion of celestial objects. But we must question researchers’ conclusion that the Mechanism incorrectly represented the orbit of Mars, in particular, by roughly 30 degrees during retrograde motion.
This discrepancy seems anomalous in a sophisticated device that otherwise exhibited a much smaller range of error. So maybe there is some other explanation.
Tags: ancient astronomy, Antikythera Mechanism, Bronze Age catastrophes, Immanuel Velikovsky, Jupiter, Mars, planetary science, Revised Venus Theory, venus
 Sekhmet (“The Mighty One”), lioness goddess of ancient Egypt, spread terror with her bloody rampages. Yet she became the protector of kings and a favorite personal goddess of millions of Egyptians.
Sekhmet (“The Mighty One”), lioness goddess of ancient Egypt, spread terror with her bloody rampages. Yet she became the protector of kings and a favorite personal goddess of millions of Egyptians.



 What reality lay behind ancient China’s flood legends? Who was the Yellow Emperor? Who was Archer Yi, what was his vermilion bow, how did he shoot down nine of ten suns, and why were there ten suns in the first place?
What reality lay behind ancient China’s flood legends? Who was the Yellow Emperor? Who was Archer Yi, what was his vermilion bow, how did he shoot down nine of ten suns, and why were there ten suns in the first place? Once a leading theory of the origin of the Earth-Moon system, the Capture Theory is simple and intuitively plausible. The numerous instances of moons with retrograde orbits show that capture is fairly common. The lunar orbit’s three moments of inertia are consistent with a past very eccentric orbit, suggestive of capture
Once a leading theory of the origin of the Earth-Moon system, the Capture Theory is simple and intuitively plausible. The numerous instances of moons with retrograde orbits show that capture is fairly common. The lunar orbit’s three moments of inertia are consistent with a past very eccentric orbit, suggestive of capture There’s no shortage of candidates for the cause of the mass extinctions of prehistory. But experts have found flaws in every one.
There’s no shortage of candidates for the cause of the mass extinctions of prehistory. But experts have found flaws in every one.
 originally formed a single planet outside the orbit of Jupiter. Early in Solar System history, Jupiter’s powerful gravitational field pulled this planet past the gas giant. As the planet neared Jupiter, tidal friction heated it to the melting point, and Jupiter tore Mars away from Earth, leaving the Pacific Basin and an array of evidence on both planets. Earth and Mars then sped off into the inner solar system.
originally formed a single planet outside the orbit of Jupiter. Early in Solar System history, Jupiter’s powerful gravitational field pulled this planet past the gas giant. As the planet neared Jupiter, tidal friction heated it to the melting point, and Jupiter tore Mars away from Earth, leaving the Pacific Basin and an array of evidence on both planets. Earth and Mars then sped off into the inner solar system.
 n and scientific researcher Kenneth J. Dillon explains his The Martian Theory of Mass Extinctions. For most of the past 4 billion years, the orbits of Mars and Earth were more eccentric than at present, and they intersected. The closest approaches of Mars led to the great mass extinctions of prehistory, while more distant approaches might account for many minor extinctions as well. The theory shows why the extinctions were serial events, why they differed in size, how they shaped the surface of Mars, and what made them so terrifically devastating. For further information, see https://www.scientiapress.com/extinctions.
n and scientific researcher Kenneth J. Dillon explains his The Martian Theory of Mass Extinctions. For most of the past 4 billion years, the orbits of Mars and Earth were more eccentric than at present, and they intersected. The closest approaches of Mars led to the great mass extinctions of prehistory, while more distant approaches might account for many minor extinctions as well. The theory shows why the extinctions were serial events, why they differed in size, how they shaped the surface of Mars, and what made them so terrifically devastating. For further information, see https://www.scientiapress.com/extinctions.
