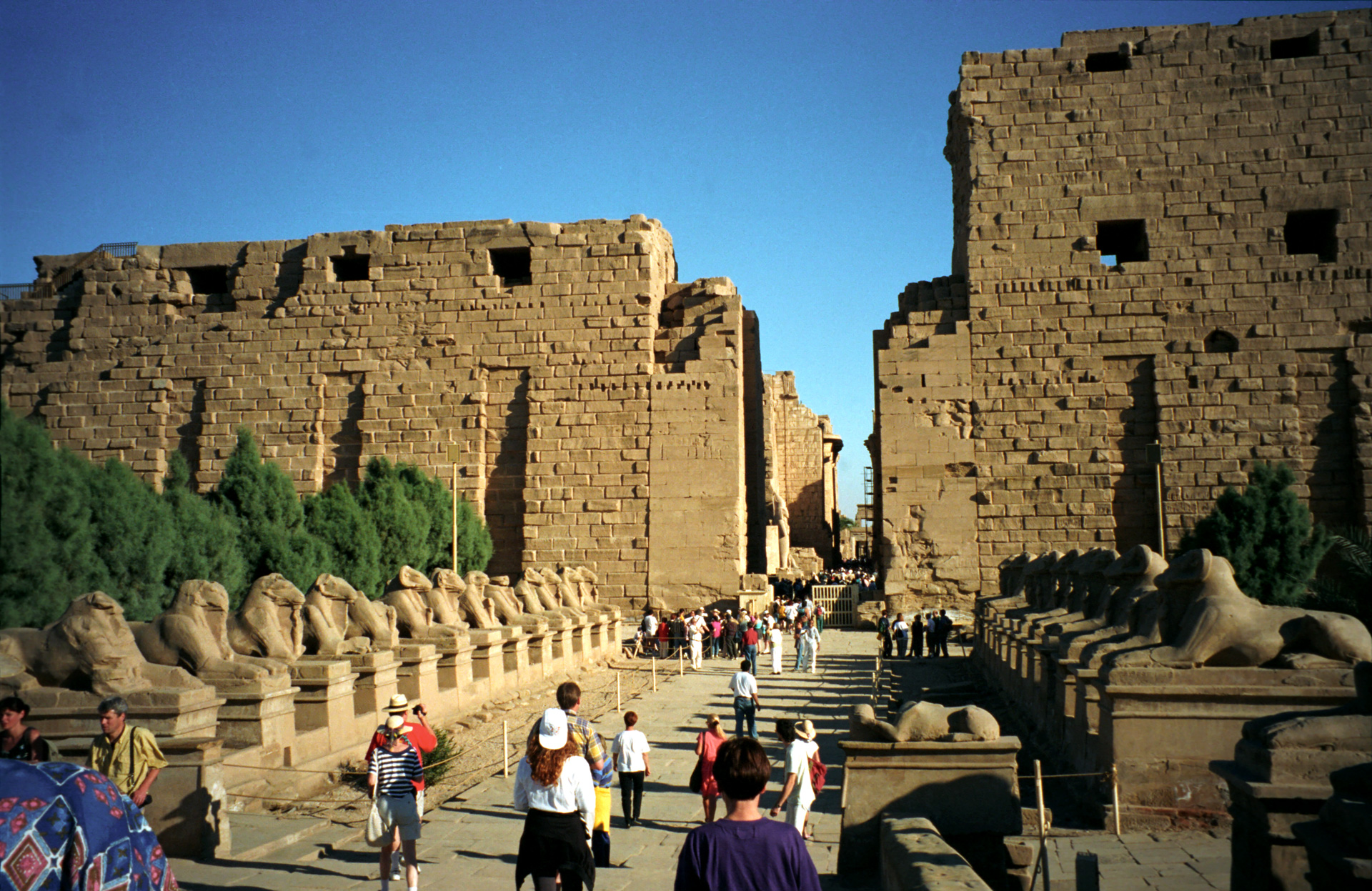
 Sometimes we just need to listen carefully. Definitely in regard to Karnak.
Sometimes we just need to listen carefully. Definitely in regard to Karnak.
Egyptian priests told Herodotus, a careful listener, that four times since Egypt had become a kingdom “the Sun rose contrary to his wont; twice he rose where he now sets, and twice he set where he now rises.”
This evidence, and much else, was interpreted by
Tags: alignment, Amon-Re, Ancient Egypt, archaeoastronomy, Gerald Hawkins, Herodotus, inversion, Karnak, Khonsupakerod, Middle Kingdom, New Kingdom, Norman Lockyer, orientation, Serabit el Khadim, Tanis, temples, Theban Hills, Velikovsky, venus
 Viktoria Nagudi interviews Kenneth J. Dillon of Scientia Press about his Theory of the Red Blood Cells. According to the theory, the red blood cells, acting as a metacolony in real time, form the dermal-optic photoreceptor, the animal magnetoreceptor, the solution to the binding problem of consciousness, the ultrasensitive Psi receptor, and the chemiluminescent Original Immune System. See also https://www.scientiapress.com/theory-of-the-red-blood-cells and Kenneth J. Dillon, Rosemarie: a Novel of Discovery Science. Washington, D.C.: Scientia Press, 2021.
Viktoria Nagudi interviews Kenneth J. Dillon of Scientia Press about his Theory of the Red Blood Cells. According to the theory, the red blood cells, acting as a metacolony in real time, form the dermal-optic photoreceptor, the animal magnetoreceptor, the solution to the binding problem of consciousness, the ultrasensitive Psi receptor, and the chemiluminescent Original Immune System. See also https://www.scientiapress.com/theory-of-the-red-blood-cells and Kenneth J. Dillon, Rosemarie: a Novel of Discovery Science. Washington, D.C.: Scientia Press, 2021.
Theory of the Red Blood Cells
Tags: binding problem of consciousness, cellular basis of consciousness, dermal optics, magnetoreception, psi receptor
Historia n and scientific researcher Kenneth J. Dillon explains his The Martian Theory of Mass Extinctions. For most of the past 4 billion years, the orbits of Mars and Earth were more eccentric than at present, and they intersected. The closest approaches of Mars led to the great mass extinctions of prehistory, while more distant approaches might account for many minor extinctions as well. The theory shows why the extinctions were serial events, why they differed in size, how they shaped the surface of Mars, and what made them so terrifically devastating. For further information, see https://www.scientiapress.com/extinctions.
n and scientific researcher Kenneth J. Dillon explains his The Martian Theory of Mass Extinctions. For most of the past 4 billion years, the orbits of Mars and Earth were more eccentric than at present, and they intersected. The closest approaches of Mars led to the great mass extinctions of prehistory, while more distant approaches might account for many minor extinctions as well. The theory shows why the extinctions were serial events, why they differed in size, how they shaped the surface of Mars, and what made them so terrifically devastating. For further information, see https://www.scientiapress.com/extinctions.
The Martian Theory of Mass Extinctions
Tags: Bronze Age catastrophes, Chicxulub, Cretaceous-Paleogene, Deccan Traps, Elysium Mons, inner solar system, Mars, mass extinctions, mass wasting, Olympus Mons, Tharsis, tidal locking, Velikovsky, venus
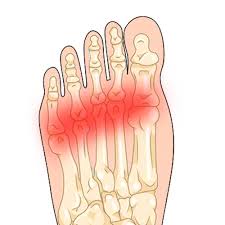 Metatarsalgia, pain in the metatarsal/forefoot area, is a common foot problem. In milder cases, it can be managed with pads, supportive footwear, adequate rest, NIAIDs, and other remedies. However, some cases become more severe over time. They cause considerable pain and undermine mobility. Among the treatments that help manage the syndrome, prolotherapy has won a number of adherents. It involves injections of dextrose, often mixed with an anesthetic. The injections stimulate natural healing. But prolotherapy is not necessarily the best option.
Metatarsalgia, pain in the metatarsal/forefoot area, is a common foot problem. In milder cases, it can be managed with pads, supportive footwear, adequate rest, NIAIDs, and other remedies. However, some cases become more severe over time. They cause considerable pain and undermine mobility. Among the treatments that help manage the syndrome, prolotherapy has won a number of adherents. It involves injections of dextrose, often mixed with an anesthetic. The injections stimulate natural healing. But prolotherapy is not necessarily the best option.
Tags: Biophotonic Therapy, low-intensity laser, metatarsalgia, podiatry, prolotherapy
 In this video, Tom Lowe, director of Physicians Awareness UBI, and Kenneth J. Dillon, author of Healing Photons, discuss the history, science, challenges, and promise of Biophotonic Therapy. Also known as ultraviolet blood irradiation, BT treats small amounts of blood with light in extracorporeal or intravenous modes. BT was invented by Emmet Knott in the 1920s. Hundreds of clinical studies have shown its effectiveness in various indications, e.g., against childhood asthma. Thousands of practitioners around the world use it to treat a wide range of disorders. BT is the leading phototherapeutic treatment of infectious diseases.
In this video, Tom Lowe, director of Physicians Awareness UBI, and Kenneth J. Dillon, author of Healing Photons, discuss the history, science, challenges, and promise of Biophotonic Therapy. Also known as ultraviolet blood irradiation, BT treats small amounts of blood with light in extracorporeal or intravenous modes. BT was invented by Emmet Knott in the 1920s. Hundreds of clinical studies have shown its effectiveness in various indications, e.g., against childhood asthma. Thousands of practitioners around the world use it to treat a wide range of disorders. BT is the leading phototherapeutic treatment of infectious diseases.
Tags: Biophotonic Therapy, biophotons, chemiluminescence, Emmet Knott, infectious diseases, intravenous laser therapy, red blood cells, UBI, ultraviolet, Ultraviolet Blood Irradiation
Among the deepest mysteries of ancient Egypt  is the Great Sphinx of Giza. Researchers, both professional and amateur, have painstakingly investigated its every aspect. Yet key puzzles remain, above all the question of why this colossal structure, the ancient world’s largest monument, was built in the first place.
is the Great Sphinx of Giza. Researchers, both professional and amateur, have painstakingly investigated its every aspect. Yet key puzzles remain, above all the question of why this colossal structure, the ancient world’s largest monument, was built in the first place.
It’s not that serious researchers and free-ranging speculators have not proposed explanations. But every theory put forward falls well short of true persuasiveness or stumbles over inconvenient facts. Here are three anomalies a correct theory should explain.
Tags: Ancient Egypt, Bronze Age catastrophes, Giza, Great Sphinx, Khafre, myth, pyramids, Re Horakhty, Sekhmet, Sphinx, Velikovsky, venus
 The civilizations of Mesoamerica were full of mysteries. What explains their fixation on Venus? What led them to develop their intricate, highly precise calendars? What can explain the little pecked-cross circles embedded in the landscape? Why were these peoples so keenly bent on human sacrifice? What were the Aztecs referring to when they said that this was the age of the Fifth Sun?
The civilizations of Mesoamerica were full of mysteries. What explains their fixation on Venus? What led them to develop their intricate, highly precise calendars? What can explain the little pecked-cross circles embedded in the landscape? Why were these peoples so keenly bent on human sacrifice? What were the Aztecs referring to when they said that this was the age of the Fifth Sun?
Fortunately, there is a skeleton key that can unlock these old secrets.
Tags: archaeoastronomy, Aztec, ball game, catastrophes, inversion of Earth, Mars, Maya, Mesoamerica, Olmec, pecked-cross circles, synodical year, Teotihuacan, Toltec, Velikovsky, venus
 Wouldn’t it be wonderful to master techniques that can lead to breakthroughs in your research? No doubt you already have your own arsenal of qualitative methods, but we all can benefit from learning more. For your consideration, here are five approaches to the various techniques used to arrive at the findings in the articles and books on this Website:
Wouldn’t it be wonderful to master techniques that can lead to breakthroughs in your research? No doubt you already have your own arsenal of qualitative methods, but we all can benefit from learning more. For your consideration, here are five approaches to the various techniques used to arrive at the findings in the articles and books on this Website:
Tags: Scientific Detective Techniques
What makes a theory good? In his canonical 1991 book Inference to the Best Explanation, Peter Lipton attempts to answer this fraught question. The philosopher identifies eleven explanatory virtues that are often placed within four groupings: evidential, coherential, aesthetic, and diachronic. Two others, James Beebe and Kenneth Dillon, draw upon the same categorical schema to present four other virtues for consideration. All fifteen are listed and defined in the following table:
Tags: explanatory virtues, explanatory virtues of an hypothesis, notional scoring, Peter Lipton, philosophy of science, scientific theory



 Viktoria Nagudi interviews Kenneth J. Dillon of Scientia Press about his Theory of the Red Blood Cells. According to the theory, the red blood cells, acting as a metacolony in real time, form the dermal-optic photoreceptor, the animal magnetoreceptor, the solution to the binding problem of consciousness, the ultrasensitive Psi receptor, and the chemiluminescent Original Immune System. See also https://www.scientiapress.com/theory-of-the-red-blood-cells and Kenneth J. Dillon,
Viktoria Nagudi interviews Kenneth J. Dillon of Scientia Press about his Theory of the Red Blood Cells. According to the theory, the red blood cells, acting as a metacolony in real time, form the dermal-optic photoreceptor, the animal magnetoreceptor, the solution to the binding problem of consciousness, the ultrasensitive Psi receptor, and the chemiluminescent Original Immune System. See also https://www.scientiapress.com/theory-of-the-red-blood-cells and Kenneth J. Dillon,  n and scientific researcher Kenneth J. Dillon explains his The Martian Theory of Mass Extinctions. For most of the past 4 billion years, the orbits of Mars and Earth were more eccentric than at present, and they intersected. The closest approaches of Mars led to the great mass extinctions of prehistory, while more distant approaches might account for many minor extinctions as well. The theory shows why the extinctions were serial events, why they differed in size, how they shaped the surface of Mars, and what made them so terrifically devastating. For further information, see https://www.scientiapress.com/extinctions.
n and scientific researcher Kenneth J. Dillon explains his The Martian Theory of Mass Extinctions. For most of the past 4 billion years, the orbits of Mars and Earth were more eccentric than at present, and they intersected. The closest approaches of Mars led to the great mass extinctions of prehistory, while more distant approaches might account for many minor extinctions as well. The theory shows why the extinctions were serial events, why they differed in size, how they shaped the surface of Mars, and what made them so terrifically devastating. For further information, see https://www.scientiapress.com/extinctions. Metatarsalgia, pain in the metatarsal/forefoot area, is a common foot problem. In milder cases, it can be managed with pads, supportive footwear, adequate rest, NIAIDs, and other remedies. However, some cases become more severe over time. They cause considerable pain and undermine mobility. Among the treatments that help manage the syndrome, prolotherapy has won a number of adherents. It involves injections of dextrose, often mixed with an anesthetic. The injections stimulate natural healing. But prolotherapy is not necessarily the best option.
Metatarsalgia, pain in the metatarsal/forefoot area, is a common foot problem. In milder cases, it can be managed with pads, supportive footwear, adequate rest, NIAIDs, and other remedies. However, some cases become more severe over time. They cause considerable pain and undermine mobility. Among the treatments that help manage the syndrome, prolotherapy has won a number of adherents. It involves injections of dextrose, often mixed with an anesthetic. The injections stimulate natural healing. But prolotherapy is not necessarily the best option. In this video, Tom Lowe, director of Physicians Awareness UBI, and Kenneth J. Dillon, author of Healing Photons, discuss the history, science, challenges, and promise of Biophotonic Therapy. Also known as ultraviolet blood irradiation, BT treats small amounts of blood with light in extracorporeal or intravenous modes. BT was invented by Emmet Knott in the 1920s. Hundreds of clinical studies have shown its effectiveness in various indications, e.g., against childhood asthma. Thousands of practitioners around the world use it to treat a wide range of disorders. BT is the leading phototherapeutic treatment of infectious diseases.
In this video, Tom Lowe, director of Physicians Awareness UBI, and Kenneth J. Dillon, author of Healing Photons, discuss the history, science, challenges, and promise of Biophotonic Therapy. Also known as ultraviolet blood irradiation, BT treats small amounts of blood with light in extracorporeal or intravenous modes. BT was invented by Emmet Knott in the 1920s. Hundreds of clinical studies have shown its effectiveness in various indications, e.g., against childhood asthma. Thousands of practitioners around the world use it to treat a wide range of disorders. BT is the leading phototherapeutic treatment of infectious diseases. 




